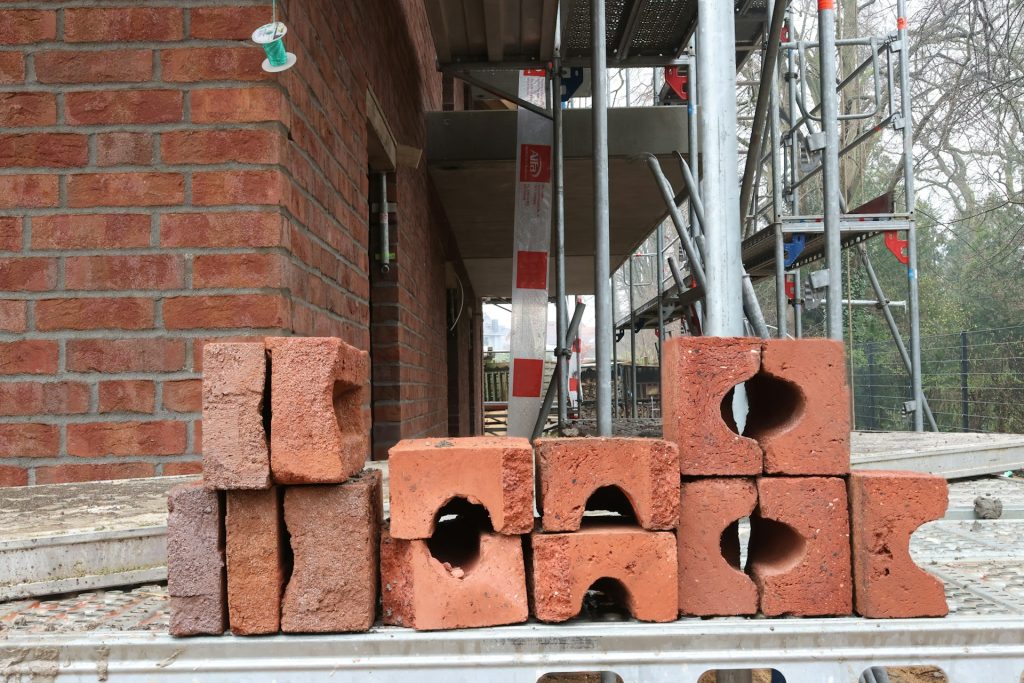
Brick is a construction material used for build walls and various structures using mortar. Brick is an artificial stone, most often made from a clay or lime-sand mixture. It has the shape of a rectangular block with dimensions of 19.4 cm × 9.2 cm × 5.7 cm.
There are many types of bricks depending on the production and molding methods, materials used, sizes, quality, physical properties, texture, application, etc.
Types of bricks
By material
- Ceramic – the most commonly used clay brick, which is fired in kilns at a temperature of 800 – 1000 °C. It has a characteristic Brick Red color.
- Silicate – white brick made from a lime-sand mixture and processed with steam under pressure and at a temperature of about 200 °C. Compared to ceramic, it is cheaper, but has a number of disadvantages – high moisture absorption (absorbs moisture), thermal conductivity (colder wall), density (heavy), as well as low heat resistance and frost resistance.
- Mudbrick – made from clay soil with the addition of straw or other plant materials. Used in dry climates for low-rise construction.
By use
- Ordinary brick is used to build walls and other structures.
- Solid – has a monolithic structure, possesses maximum strength and resistance to mechanical impact.
- Hollow – in the thickness of the brick there are voids filled with air, which can make up to 25% of the volume. Such a brick is lighter, the voids reduce thermal conductivity and increase sound insulation.
- Facing brick – serves for external finishing, but is universal, performing both a structural and decorative role. Protects the building from mechanical impact and weather conditions. Must be durable, have low water absorption, high frost resistance, light resistance. Facing bricks can be of a wide variety of colors, textures and shapes.
- Clinker brick is a type of particularly strong brick that is made from a special type of clay and exposed to excessive heat during the firing process, sintering the surface of the brick and forming a shiny, dark-colored coating. It can have many shades, has increased strength, water resistance and frost resistance, which allows it to be used even for laying sidewalks.
- Glazed – the front sides of the brick are covered with a special glaze mixture, which consists of industrial glass and dyes, after which the brick is fired again. It is used for finishing and decorating facades, but is used quite rarely due to its high cost and fragility before installation.
- Firebrick – designed for the construction of stoves, fireplaces, chimneys and other structures that are in direct contact with fire and high temperatures. The brick must have high heat resistance, thermal stability (withstand many heating and cooling cycles), low thermal conductivity (to retain heat), as well as high thermal inertia and heat capacity.
- Fireclay brick is made from refractory ceramic mass, in the production of which quartz sand, crushed fire-resistant clay and fireclay powder are used.
- Chemically resistant or acid-resistant – a special type of brick for use in aggressive environments and resistant to chemical reactions. It is used in industrial furnaces and the chemical industry. It is made from special materials, fired for a longer time and at higher temperatures.
By manufacture method
- Burnt – after molding, the brick is fired in kilns, which makes it strong and durable.
- Chemically set – bricks are not fired during production, but harden due to the properties of the materials used. This includes silicate (lime) or concrete (cement) bricks.
- Hyper-pressed – brick is produced using high pressure, the main material is screenings from the development of limestone rocks.
Brick sizes
Historically, different countries have their own standards for brick sizes, but they do not differ much from each other. For ease of use, the brick fits in one hand in size and weight if you grasp it by width (about 10 cm) between your thumb and index finger; the length is usually twice the width (about 20 cm).
Such standard brick sizes allow for the creation of effective bonding in masonry, that is, overlapping the seams in adjacent rows. The large flat side of the brick is called the bed, the long side is called the stretcher, and the short side is called the header.
| Country | In millimetrs | In inches |
|---|---|---|
| Australia | 230 × 110 × 76 | 9.1 × 4.3 × 3.0 |
| China | 240 × 155 × 53 | 9.4 × 6.1 × 2.1 |
| Denmark | 228 × 108 × 54 | 9.0 × 4.3 × 2.1 |
| Germany | 240 × 115 × 71 | 9.4 × 4.5 × 2.8 |
| India | 228 × 107 × 69 | 9.0 × 4.2 × 2.7 |
| Japan | 210 × 100 × 60 | 8.3 × 3.9 × 2.4 |
| Russia | 250 × 120 × 65 | 9.8 × 4.7 × 2.6 |
| South Africa | 222 × 106 × 73 | 8.7 × 4.2 × 2.9 |
| Sweden | 250 × 120 × 62 | 9.8 × 4.7 × 2.4 |
| United Kingdom | 215 × 102.5 × 65 | 8.5 × 4.0 × 2.6 |
| United States | 194 × 92 × 57 | 7.6 × 3.6 × 2.2 |
In addition to standard bricks, bricks of other sizes and shapes are produced, which are used for special purposes. For example, there are one and a half or double bricks, which are one and a half or two times thicker than the standard, which allows for faster laying and less mortar consumption.
Brick weight
The weight of a brick directly depends on its density, the material from which it is made, its size and purpose.
The weight of a standard ceramic brick is about 2.5 kg, hollow about 2 kg. A solid silicate brick weighs about 3 kg, hollow about 2.5 kg. The weight of a firebrick is about 3-4 kg.